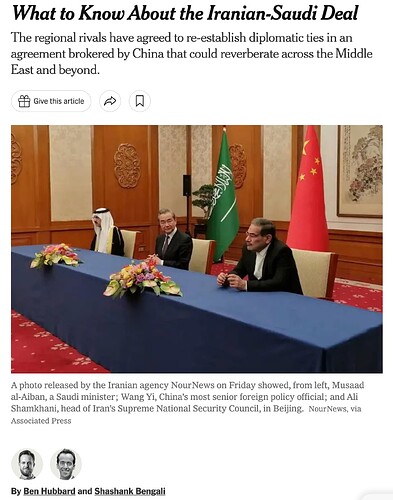
-
伊朗和沙特阿拉伯已经宣布重新建立外交关系,这可能导致中东地区的重大调整。
-
这对美国来说是一个地缘政治挑战,但对促成两国谈判的中国来说却是一个胜利。
-
该协议包括恢复安全合作条约,重新开放大使馆,恢复贸易、投资和文化协议。
-
这两个波斯湾国家之间的竞争植根于宗教和政治方面的分歧。
-
简单的外交接触可能不足以克服这些分歧。
-
围绕该协议还有许多关键问题,如对地区稳定和美国在中东地区的地位的影响。
-
几十年来,沙特阿拉伯和伊朗一直在争夺影响力。
-
2016年,伊朗的抗议者袭击了沙特的外交使团,两国之间的紧张关系加剧。
-
沙特鼓励西方对伊朗的核计划作出严厉回应,并建立了通往以色列的外交后方渠道,以应对来自德黑兰的威胁。
-
沙特阿拉伯和伊朗之间的外交关系在周五宣布取得突破性进展。
-
目前还不清楚这将如何影响沙特阿拉伯参与以色列和美国对抗伊朗的努力。
-
新的外交接触可能会使沙特阿拉伯和伊朗走到一起,从而搅乱中东和其他地区的地缘政治。
-
沙特阿拉伯和伊朗都把自己看作是地区大国和世界19亿穆斯林的支柱。
-
这两个地区大国之间恢复外交关系至少标志着长期以来影响中东的冷战的部分解冻。
-
伊朗和沙特阿拉伯的领导人在2016年断绝了外交关系,此后一直在进行口头上的争吵。
-
两国之间的敌意已经超过了口头上的,导致了整个中东地区在伊拉克、黎巴嫩、叙利亚和也门的冲突。
-
也门的冲突最为严重,沙特的炸弹炸死了平民,而伊朗支持的叛军则以导弹和无人机作为回应。
-
周五,两国的外交关系出现了一个令人惊讶的突破。
-
近年来,沙特和伊朗的情报主管一直在伊拉克会面,讨论地区安全问题。
-
更加正式的外交接触可能为在冷却地区热点方面取得进一步进展提供途径。
-
两国之间的敌意已经不仅仅是口头上的,而是在整个中东地区的冲突中发挥着作用。
-
中国主持了伊朗和沙特阿拉伯之间的会谈,并达成了协议,突出了中国在该地区日益增长的影响力。
-
中国不干涉其他国家事务的政策得到了地区领导人的赞赏。
-
中国希望该地区保持稳定,因为他们从海湾地区获得了很大一部分能源。
-
中国提出了全球安全倡议和乌克兰和平计划,这两项计划在西方被批评为促进中国利益。
-
中国的外交政策官员说,该协议是 “对世界的重大利好消息”,并鼓励中东国家加强团结与合作,摒弃外部干扰。
-
中国正试图在世界舞台上发挥更大的外交作用,伊朗和沙特之间的协议凸显了中国在该地区日益增长的政治和经济影响力。
-
由中国斡旋的伊朗和沙特阿拉伯之间的协议的消息使华盛顿的外交政策鹰派人士感到震惊。保护民主基金会的马克-杜博维茨说,这表明对华盛顿缺乏信任,中国正在成为中东政治中的一个大国。
-
然而,如果该协议能缓解该地区的紧张局势,拜登政府可能会受益。昆西研究所支持美国在海外的克制,并认为一个伊朗和沙特没有冲突的稳定的中东对美国有利。白宫支持任何缓和紧张局势的努力,但对伊朗履行其协议的一方表示担忧。
-
总的来说,伊朗和沙特之间的协议提醒人们,中国在中东地区的影响力越来越大,拜登政府希望看到该地区保持稳定。白宫对伊朗将履行他们的协议持谨慎的乐观态度,但仍将保持警惕,监测局势。
-
沙特阿拉伯和伊朗是伊斯兰教的两个主要教派,沙特阿拉伯代表逊尼派,伊朗代表什叶派。
-
沙特阿拉伯与美国关系密切,而伊朗强烈反对美国。
-
伊朗已投资在整个地区建立一个武装民兵网络,沙特阿拉伯认为这是对地区秩序的威胁。
-
两国之间存在分歧的领域包括。
-
伊朗支持的什叶派民兵在伊拉克和黎巴嫩的作用。
-
伊朗支持的叙利亚总统巴沙尔-阿萨德的未来。
-
伊朗支持的胡塞叛军在也门的未来,沙特阿拉伯认为胡塞叛军是国家安全的最大威胁。
-
这些分歧使沙特阿拉伯和伊朗之间的关系解冻变得复杂,两国必须解决这些问题,以促进更好的关系。
-
Iran and Saudi Arabia have announced that they are re-establishing diplomatic ties, which could lead to a major realignment in the Middle East.
-
This poses a geopolitical challenge for the United States, but is a victory for China which brokered the talks between the two countries.
-
The agreement includes reviving a security cooperation pact, reopening embassies, resuming trade, investment and cultural accords.
-
The rivalry between the two Persian Gulf nations is rooted in disagreements about religion and politics.
-
Simple diplomatic engagement may not be enough to overcome these differences.
-
There are numerous key questions surrounding the deal, such as the implications for regional stability and the US’s position in the Middle East.
-
Saudi Arabia and Iran have been competing for influence for decades.
-
Tensions between the two nations grew in 2016 when protesters in Iran stormed Saudi diplomatic missions.
-
Saudi Arabia has encouraged a harsh response from the West toward Iran’s nuclear program and established diplomatic back channels to Israel to confront the threat from Tehran.
-
A breakthrough in diplomatic relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran was announced on Friday.
-
It is unclear how this will affect Saudi Arabia’s participation in Israeli and American efforts to counter Iran.
-
The new diplomatic engagement could scramble geopolitics in the Middle East and beyond by bringing together Saudi Arabia and Iran.
-
Saudi Arabia and Iran have each seen themselves as regional powers and lodestars for the world’s 1.9 billion Muslims.
-
The resumption of diplomatic relations between the two regional powers marks at least a partial thaw in a cold war that has long shaped the Middle East.
-
The leaders of Iran and Saudi Arabia have broken off diplomatic relations in 2016 and have been trading verbal barbs since then.
-
The enmity between the two nations has been more than verbal, leading to conflicts across the Middle East in Iraq, Lebanon, Syria and Yemen.
-
The conflict has been most catastrophically in Yemen, with Saudi bombs killing civilians and Iranian-backed rebels responding with missiles and drones.
-
On Friday, there was a surprise breakthrough in diplomatic relations between the two countries.
-
Saudi and Iranian intelligence chiefs have been meeting in Iraq in recent years to discuss regional security.
-
A more formal diplomatic engagement may provide avenues for further progress in cooling regional flash points.
-
The enmity between the two nations has been more than verbal and has been playing out in conflicts across the Middle East.
-
On Friday, there was a surprise breakthrough in diplomatic relations between the two countries.
-
A more formal diplomatic engagement may provide avenues for further progress in cooling regional flash points.
-
China hosted talks between Iran and Saudi Arabia that resulted in an agreement, highlighting China’s growing influence in the region.
-
China’s policy of noninterference in other countries’ affairs is appreciated by regional leaders.
-
China wants stability in the region since they get a significant portion of their energy from the Gulf.
-
China has presented a Global Security Initiative and a peace plan for Ukraine, both of which have been criticized in the West for promoting Chinese interests.
-
China’s foreign policy official said the agreement was “major positive news for the world” and encouraged Middle Eastern countries to enhance unity and cooperation and cast off external interference.
-
China is attempting to play a bigger diplomatic role on the world stage and the agreement between Iran and Saudi Arabia highlights its growing political and economic clout in the region.
-
News of a deal between Iran and Saudi Arabia brokered by China alarmed foreign policy hawks in Washington. Mark Dubowitz of the Foundation for Defense of Democracies said it showed a lack of trust in Washington and that China is becoming a major power in Middle Eastern politics.
-
However, a Biden administration may benefit if the agreement reduces tensions in the region. The Quincy Institute supports U.S. restraint overseas and believes a stable Middle East where Iran and Saudi Arabia are not in conflict benefits the United States. The White House supports any effort to de-escalate tensions, but expressed concern over Iran honoring their side of the deal.
-
Overall, the deal between Iran and Saudi Arabia is a reminder of China’s growing influence in the Middle East and the Biden administration’s interest in seeing the region remain stable. The White House is cautiously optimistic that Iran will honor their side of the deal, but will remain vigilant in monitoring the situation.
-
Saudi Arabia and Iran are the two leading sects of Islam, with Saudi Arabia representing Sunnis and Iran representing Shiites.
-
Saudi Arabia has close ties with the United States, which Iran strongly opposes.
-
Iran has invested in building an armed militia network across the region, which Saudi Arabia considers a threat to regional order.
-
Areas of disagreement between the two countries include:
-
The role of Iranian-backed Shiite militias in Iraq and Lebanon.
-
The future of President Bashar al-Assad in Syria, whom Iran has supported.
-
The future of the Iranian-backed Houthi rebels in Yemen, whom Saudi Arabia considers a top national security threat.
-
These disagreements have complicated the thaw in relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran, and both countries must address these issues in order to foster better relations.
链接:What to Know About the Iran-Saudi Deal - The New York Times